NAIway Translation Service – Your Expert in Korean Translation
NAIway Translation Service offers professional Korean translation across a wide range of specialized fields, including business, law, engineering, IT, manuals, menus, SDS, and more. Our team consists of experienced Japan-based and native Korean translators, ensuring accurate, high-quality translations with local expertise. By working with on-site professionals, we eliminate time zone delays, providing fast and efficient services.
Why Choose NAIway for Korean Translation?
NAIway – The Pathway to Seamless Korean Translation.
Korean and Japanese share a close geographical and linguistic relationship, making translation between the two languages more seamless compared to other language pairs. Their similar grammar structures and cultural influences reduce potential discrepancies.
However, Korean has its unique linguistic characteristics, such as:
- Homonyms requiring contextual interpretation
- Age- and gender-specific honorifics and titles
- Distinct differences between spoken and written language, as well as formal and casual expressions
Capturing these nuances is crucial for delivering accurate and natural translations. At NAIway, our skilled translators and rigorous quality control ensure precise, culturally adapted translations that maintain the original intent and tone.

For more details, please feel free to contact us.
Korean Translation Rates
Below are NAIway’s standard translation rates.
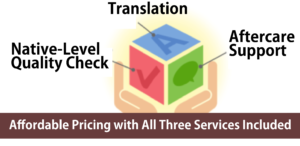
Our regular translation fees cover all of the following services, so you can rely on us with confidence.
Translation
+
Native-Level Quality Check
+
After-Support※
※ As part of our after-support, we handle revisions and inquiries within the post-delivery verification period (typically one week).
(Please note that changes or additions to the original document are not included.)
Japanese to Korean Translation
From 13.86 JPY per character
Korean to Japanese Translation
From 15.4 JPY per character
- The actual cost will be estimated based on the content and volume of the document. Please send us the document when requesting a quote.
- Minimum Charge Policy. Depending on the character/word count and other conditions, we have a two-tier minimum charge system of 5,500 Japanese Yen or 11,000 Japanese Yen (tax included). This ensures coverage of the essential costs involved in translation coordination and quality assurance.
For more details, please feel free to contact us.
Key Points for Korean Translation
The Subtle Art of Korean-Japanese Translation
Korean and Japanese have influenced each other over time and share similar grammatical structures. However, simply substituting words one-for-one does not create natural, authentic Korean that resonates with native speakers or fluent, seamless Japanese that feels right to its audience.
Korean expressions tend to be more direct and explicit compared to Japanese. For example, the commonly used Japanese phrase "~だと思います" ("Dato Omoimasu" in Japanese "I think…" in English) carries an element of ambiguity that Koreans rarely use. Additionally, passive expressions and double negatives, which feel natural in Japanese, often sound awkward to Korean ears.
Honorifics also pose a unique challenge. Korean honorifics are deeply rooted in cultural traditions, making terms of address for superiors more complex and often impossible to translate directly into Japanese.
To achieve a truly natural translation, it is essential to understand the cultural and linguistic nuances of both languages. Only by doing so can we convey the original meaning accurately, ensuring Korean feels naturally Korean and Japanese remains fluid and authentic without awkwardness.

Send Us Your Document for a Quick Quote!
Multilingual Translation Support
At NAIway, we offer multilingual translation services. In addition to Korean, we provide English, Chinese, and other language translations, allowing you to handle multiple language requests all in one place.
By consolidating your translations with us, you can save time, ensure consistency, and maintain high-quality standards across all languages. Feel free to contact us for more details!

NAIway's Quality Assurance System
At NAIway Translation Service, we believe that quality management is our top priority as a professional translation company. To ensure the highest standards, we have developed our own Quality Assurance System (QAS) and implement strict quality control measures.
For high-quality Japanese-Korean and Korean-Japanese translations, every document undergoes a two-step review process: after the initial translation, a second translator conducts a thorough quality check.
We meticulously review each character and sentence, ensuring logical flow, terminology consistency, and appropriate expressions to deliver a refined translation tailored to your needs.

Introduction to Our Korean Translators
Here are some of the translators currently working with or registered at NAIway.
For more details, please feel free to contact us.
What is the Korean Language?
The Korean Language: An Overview
Korean is the official language of both the Republic of Korea (South Korea) and the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (North Korea). Beyond these countries, it is also spoken by ethnic Koreans in China’s northeastern region, Korean Americans who emigrated to the U.S. after the war, and Zainichi Koreans (ethnic Koreans residing in Japan). The total number of Korean speakers is estimated to be around 75 million.
In South Korea, the language is commonly referred to as "한국어" (Hanguk-eo, Korean), while in North Korea, it is called "조선어" (Choson-eo, Choson language). Additionally, due to the use of the Hangul writing system, some refer to it as "Hangul language." In Western countries, it is known as "Korean," derived from the historical kingdom of Goryeo (Koryo).
Korean shares strong linguistic similarities with Japanese, making cultural and linguistic discrepancies less pronounced compared to other language pairs.
The Korean Writing System
Korean is written using the Hangul script. The name "Hangul" (한글) comes from "Han" (한), meaning "great" or "grand," and "Gul" (글), meaning "script" or "letters," which together translate to "the great script."
Hangul consists of 21 vowels and 19 consonants, which are systematically combined to form characters. It is designed to visually represent the shape of the mouth and tongue during pronunciation, making it one of the most scientifically structured writing systems in the world.
"Hello" in Korean
The Korean word for "Hello" is "안녕하세요" (Annyeonghaseyo).
This is the most common and polite way to greet someone in Korean. It can be used in both formal and semi-formal settings.
The History of Hangul
Until the 15th century, Korean was primarily written using Chinese characters (Hanja). However, since Chinese characters were originally designed for the Chinese language, they were difficult to use for Korean and were mainly reserved for the nobility and government officials.
To address this, the 4th king of the Joseon Dynasty, King Sejong, collaborated with scholars to create a new writing system known as "Hunminjeongeum" (훈민정음)—the original name for Hangul. The name means "The Correct Sounds for the Instruction of the People."
The newly developed script and its explanation were compiled into a book titled "Hunminjeongeum", which was published and made available to the public. Although the name was later changed to "Hangul" in the early 20th century, the date of its original publication is now celebrated in South Korea as "Hangul Day."
Since Hangul was developed independently of existing writing systems and became the country's official script, it is recognized by linguists worldwide for its unique and scientific structure.
Main Regions Where Korean is Spoken
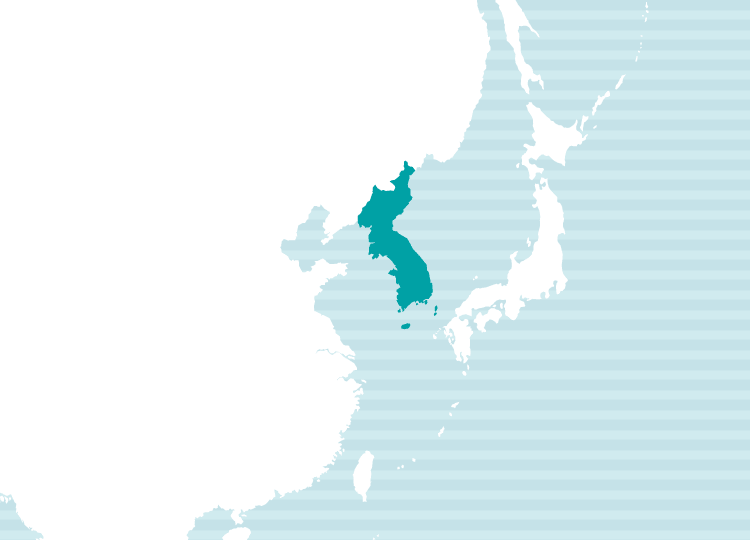
Language Classification & Usage Regions
Spoken In: South Korea, North Korea, parts of China, and other regions
Language Family: Koreanic (Korean Language Family)
Similarities Between Korean and Japanese
Korean and Japanese share a similar sentence structure, following the Subject-Object-Verb (SOV) order. Additionally, both languages use particles (such as "は" (wa) and "を" (wo) in Japanese) to indicate grammatical relationships between words.
Since both languages historically used Chinese characters (Hanja/Kanji), many words have similar pronunciations in Japanese and Korean. Examples include:
- 気分(kibun) → 기분 (kibun)
- 約束 (yakusoku)→ 약속 (yaksok)
- 無料(muryo) → 무료 (muryo)
- 基準 (kijyun)→ 기준 (kijun)
- 家族(kazoku) → 가족 (kajok)
- 簡単(kantan) → 간단 (kandan)
- 調味料(chomiryo) → 조미료 (chomiryo)
These linguistic similarities make it easier for Japanese speakers to learn Korean and vice versa.


