At NAIway Translation Service, we provide high-quality Japanese-Vietnamese and Vietnamese-Japanese translations, handled by experienced professionals specialized in various fields. Our service ensures accuracy and cultural relevance, adapting to the content and purpose of each translation.
Vietnam has experienced remarkable economic growth, attracting increasing attention from Japanese companies expanding into retail, food service, logistics, tourism, and entertainment. Additionally, Vietnam is recognized as a key source of skilled talent, further driving demand for Vietnamese translation.
Vietnamese is now one of the most sought-after languages for translation, following Chinese and Korean. The demand extends beyond business documents and operation manuals to market research, contracts, product catalogs, corporate and school brochures, websites, and more.
As the number of Vietnamese visitors to Japan continues to rise, the need for clear and engaging multilingual content is growing. With 70% of Vietnamese tourists visiting Japan for the first time, their interests have shifted from shopping to experiential tourism. This trend highlights the importance of translating guide maps, transportation information, event details, facility notices, and safety instructions. Additionally, social media and video content play a vital role in inbound marketing, making multifaceted translation services essential.
With NAIway, you can bridge the language gap and connect seamlessly with the Vietnamese market.

For more details, please feel free to contact us.
Vietnamese Translation Rates (Japanese-Vietnamese & Vietnamese-Japanese)
Below are NAIway’s standard translation rates.
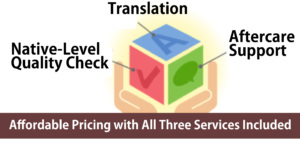
Our regular translation fees cover all of the following services, so you can rely on us with confidence.
Translation
+
Native-Level Quality Check
+
After-Support※
※ As part of our after-support, we handle revisions and inquiries within the post-delivery verification period (typically one week).
(Please note that changes or additions to the original document are not included.)
Japanese to Vietnamese Translation
From 20.9 JPY per character
Vietnamese to Japanese Translation

From 28.6 JPY per word
- The actual cost will be estimated based on the content and volume of the document. Please send us the document when requesting a quote.
- Minimum Charge Policy. Depending on the character/word count and other conditions, we have a two-tier minimum charge system of 5,500 Japanese Yen or 11,000 Japanese Yen (tax included). This ensures coverage of the essential costs involved in translation coordination and quality assurance.
For more details, please feel free to contact us.
NAIway's Quality Assurance System
At NAIway Translation Service, we believe that quality management is our top priority as a professional translation company. To ensure the highest standards, we have developed our own Quality Assurance System (QAS) and implement strict quality control measures.
For high-quality Japanese-Vietnamese and Vietnamese-Japanese translations, every document undergoes a two-step review process: after the initial translation, a second translator conducts a thorough quality check.
We meticulously review each character and sentence, ensuring logical flow, terminology consistency, and appropriate expressions to deliver a refined translation tailored to your needs.

Multilingual Translation Support
At NAIway, we offer multilingual translation services. Along with Vietnamese, we provide translations in English, Chinese, Tagalog, Thai, and more—all in one place.
If you're considering inbound tourism solutions, feel free to contact us for a consultation!

Introduction to Our Vietnamese Translators
Here are some of the translators currently working with or registered at NAIway.
For more details, please feel free to contact us.
What is the Vietnamese language?
Vietnamese is the native language of the Kinh people, who make up about 90% of Vietnam's population, and serves as the official language of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam. It is also referred to as Kinh language or Việt ngữ and is commonly used as a lingua franca among Vietnam’s ethnic minorities.
While many Southeast Asian languages have been influenced by Indian culture, Vietnam was historically under Chinese rule. As a result, much of its classical literature and historical records were written in Classical Chinese (Hán Văn), making Vietnam a part of the Sinosphere.
In ancient times, Vietnamese was written using Chữ Nôm, a unique script based on Chinese characters, adapted to represent the local language.
However, during the French colonial era, a Romanized script called Quốc Ngữ was developed by French missionaries. This system gradually replaced Chữ Nôm, and in 1945, with the establishment of the Democratic Republic of Vietnam, Quốc Ngữ was officially adopted as the standard writing system for Vietnamese.
Vietnamese Script
Vietnamese uses the Latin alphabet, enhanced with diacritical marks to indicate tones.
However, the letters F, J, W, and Z are generally not used, except in proper nouns and loanwords.
How to Say “Hello” in Vietnamese
Xin Chào/sin tʃaʊ/
Primary Regions of Use
Language Family: Austroasiatic → Mon-Khmer → Viet-Muong
Spoken In: Vietnam, Cambodia, Taiwan, the United States, France, and more.
Key Features of the Vietnamese Language
Vietnamese is considered one of the most challenging languages to pronounce in the world. As a tonal language, pronunciation is crucial, featuring six distinct tones that are unfamiliar to Japanese speakers. To speak Vietnamese accurately, one must master 12 monophthongs, 3 diphthongs, 27 initial consonants, and 8 final consonants. The same spelling can have six different pronunciations, each with a unique meaning—mispronouncing a word can lead to confusion or miscommunication. Adding to the complexity, pronunciation varies significantly across Northern, Central, and Southern dialects.
However, Vietnamese grammar is surprisingly simple. Like English, it follows the SVO (Subject-Verb-Object) structure. There are no verb conjugations for tense or person, nor any grammatical changes based on singular or plural forms. Instead, tense and subject distinctions are conveyed through word order and context.
Vietnamese has strong historical ties to the Chinese writing system, much like Japanese. Many commonly used Vietnamese words are of Chinese origin, making them familiar to Japanese speakers. For example:
- "Chú ý" (チューイー) = 注意 (Attention)
- "Quản lý" (クアンリー) = 管理 (Management)
- "Cải cách" (カイカック) = 改革 (Reform)
Recognizing these similarities can make Vietnamese feel more approachable. However, over time, some words have evolved to carry different meanings, so caution is needed when interpreting them.


