Russia, endowed with vast natural resources, plays a pivotal role as a bridge connecting Europe, Asia, and the Middle East. In this strategic region of Central Asia, Russian stands out as an essential language for international business.
At NAIway Translation Service, our seasoned linguists deliver top-tier translations across diverse industries—including economics, law, IT, engineering, healthcare, and tourism—covering everything from business documents and manuals to brochures, websites, and even gourmet menus.

For more details, please feel free to contact us.
Russian Translation Rates (Japanese-Russian & Russian-Japanese)
Below are NAIway’s standard translation rates.
Our regular translation fees cover all of the following services, so you can rely on us with confidence.
Translation
+
Native-Level Quality Check
+
After-Support※
※ As part of our after-support, we handle revisions and inquiries within the post-delivery verification period (typically one week).
(Please note that changes or additions to the original document are not included.)
Japanese to Russian Translation
From 27.5 JPY per character
Russian to Japanese Translation

From 38.5 JPY per word
- The actual cost will be estimated based on the content and volume of the document. Please send us the document when requesting a quote.
- Minimum Charge Policy. Depending on the character/word count and other conditions, we have a two-tier minimum charge system of 5,500 Japanese Yen or 11,000 Japanese Yen (tax included). This ensures coverage of the essential costs involved in translation coordination and quality assurance.
For more details, please feel free to contact us.
NAIway's Quality Assurance System
At NAIway Translation Service, we believe that quality management is our top priority as a professional translation company. To ensure the highest standards, we have developed our own Quality Assurance System (QAS) and implement strict quality control measures.
For high-quality Japanese-Russian and Russian-Japanese translations, every document undergoes a two-step review process: after the initial translation, a second translator conducts a thorough quality check.
We meticulously review each character and sentence, ensuring logical flow, terminology consistency, and appropriate expressions to deliver a refined translation tailored to your needs.

Multilingual Translation Support
At NAIway, we offer multilingual translation services. Along with Russian, we provide translations in English, Italian, Portuguese, Spanish, and more—all in one place.
If you're considering inbound tourism solutions, feel free to contact us for a consultation!

Introduction to Our Russian Translators
Here are some of the translators currently working with or registered at NAIway.
For more details, please feel free to contact us.
What is the Russian language?
Russian is the official language of the Russian Federation. It also holds official status in several former Soviet republics, including Belarus, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan.
With the largest number of native speakers in Europe, Russian is one of the six official languages of the United Nations. The language uses the Cyrillic script for writing.
Due to geographical proximity and historical ties, Japan and Russia have a long-standing relationship. As a result, many Russian loanwords have found their way into the Japanese language. Words like ajito (hideout), ikura (salmon roe), kombinat (industrial complex), seiuchi (walrus), noruma (quota), and intelli (intellectual) all have Russian origins.
Russian Script
The language is written using the Cyrillic script.
How to Say “Hello” in Russian
Здравствуйте/ˈzdrastvʊjtʲe]
Primary Regions of Use
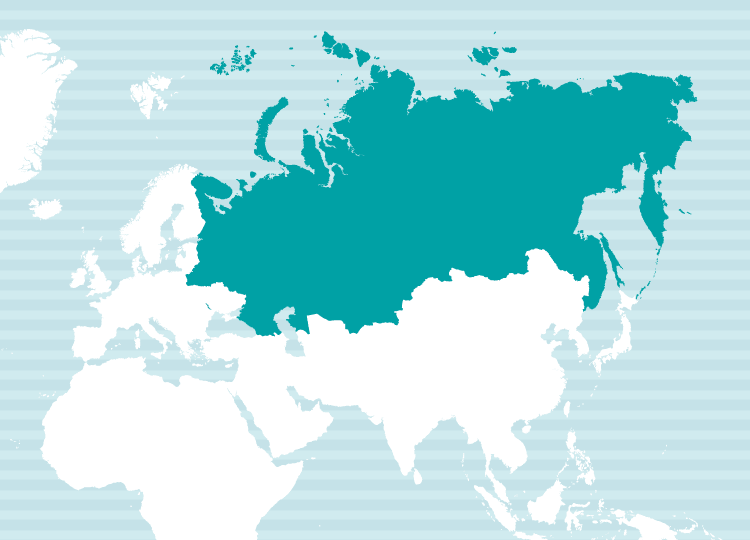
Language Family: Indo-European > Slavic > East Slavic
Regions Spoken: Russia, Azerbaijan, Armenia, Ukraine, Uzbekistan, Estonia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Georgia, Turkmenistan, Belarus, Moldova, Latvia, Lithuania, and more.
The History of the Russian Language
The Origins and Evolution of the Russian Language
There are several theories regarding the origins of the Russian language, but the most widely accepted one traces its roots to Old East Slavic, the language once spoken by the East Slavs. This language was used in the Kievan Rus’, a flourishing medieval state in Eastern Europe from the 9th century. However, with the Mongol invasions and the subsequent collapse of the Kievan Rus’, Russian came under significant influence from Tatar and Mongolic languages—particularly in areas related to finance and administration—due to the extended rule of the Mongol Empire.
By the 14th century, the Grand Duchy of Moscow had emerged, and the language used in this state gradually evolved into what we now recognize as the Russian language.
During the era of the Russian Empire, Tsar Peter the Great spearheaded a wave of language reforms. These included the simplification of the Russian script, the introduction of Arabic numerals, and the publication of Russia’s first newspapers. As Russia sought to modernize by looking to Western Europe, it adopted a vast array of technical and scientific vocabulary, borrowing heavily from Dutch, French, and German.
At the same time, French became the language of the Russian aristocracy, often spoken in daily life. This linguistic trend is reflected in 19th-century Russian literature, particularly in works like Tolstoy’s War and Peace, where French is interwoven throughout the text.
During the Soviet era, Russian became the de facto official language across the USSR, though it was never formally declared as such. It wasn’t until the formation of the Russian Federation that Russian was officially designated as the national language. After the collapse of the Soviet Union, the former republics established their own national languages as primary, yet Russian continues to be widely used in many of these regions today.


