Thailand is the only country in Southeast Asia that has never been colonized, allowing it to preserve its unique culture and language. However, English proficiency remains relatively low, making Thai translation essential for businesses expanding into Thailand and for inbound tourism strategies.
At NAIway Translation Service, we offer high-quality, natural Thai translations tailored to your needs. Our experienced specialists provide expert translations in tourism, business, law, engineering, IT, entertainment, food industries, and more—ensuring clarity and cultural accuracy in every project.

Thai Translation Rates (Japanese-Thai & Thai-Japanese)
Below are NAIway’s standard translation rates.
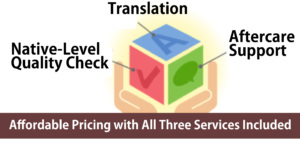
Our regular translation fees cover all of the following services, so you can rely on us with confidence.
Translation
+
Native-Level Quality Check
+
After-Support※
※ As part of our after-support, we handle revisions and inquiries within the post-delivery verification period (typically one week).
(Please note that changes or additions to the original document are not included.)
Japanese to Thai Translation
From 20.9 JPY per character
Thai to Japanese Translation

From 17.6 JPY per word
- The actual cost will be estimated based on the content and volume of the document. Please send us the document when requesting a quote.
- Minimum Charge Policy. Depending on the character/word count and other conditions, we have a two-tier minimum charge system of 5,500 Japanese Yen or 11,000 Japanese Yen (tax included). This ensures coverage of the essential costs involved in translation coordination and quality assurance.
For more details, please feel free to contact us.
The Growing Need for Thai Translation
Thailand is a pro-Japan country, and Japanese products are highly popular among Thai consumers. With many Japanese companies expanding into Thailand and establishing factories across the country, there is a growing need for Thai translations of internal documents, such as work manuals and company regulations.
In terms of inbound tourism, the 2013 visa exemption for Thai travelers to Japan led to a surge in Thai tourists. As a result, translation needs have expanded in the tourism sector, including transportation guides, restaurant menus, and travel-related information.
Additionally, Japanese manga and anime enjoy immense popularity in Thailand. While demand for Thai translations of anime and manga continues to grow, many Thai fans are also traveling to Japan to attend anime events and purchase character goods. This has created an increasing need for Thai-language content to cater to these enthusiastic visitors.

Key Points & Considerations for Thai Translation
When handling Thai text in Japan, the most critical factor to consider is the Thai script. Thai is an Indic-based phonetic writing system, utilizing various diacritical marks and tone indicators. These marks are essential for meaning, but when processed digitally, font compatibility issues can cause text corruption, misplaced symbols, or missing characters.
Another challenge is line breaks. In Thai, breaking a word incorrectly can completely alter its meaning. Unlike English, Thai does not use spaces between words, and there is no distinction between uppercase and lowercase letters. Without proper knowledge of Thai, it is difficult to determine where to break lines correctly.

NAIway's Quality Assurance System
At NAIway Translation Service, we believe that quality management is our top priority as a professional translation company. To ensure the highest standards, we have developed our own Quality Assurance System (QAS) and implement strict quality control measures.
For high-quality Japanese-Indonesian and Indonesian-Japanese translations, every document undergoes a two-step review process: after the initial translation, a second translator conducts a thorough quality check.
We meticulously review each character and sentence, ensuring logical flow, terminology consistency, and appropriate expressions to deliver a refined translation tailored to your needs.

Multilingual Translation Support
At NAIway, we offer multilingual translation services. Along with Thai, we provide translations in English, Chinese, Tagalog, Indonesian, and more—all in one place.
If you're considering inbound tourism solutions, feel free to contact us for a consultation!

For more details, please feel free to contact us.
Introduction to Our Thai Translators
Here are some of the translators currently working with or registered at NAIway.
What is the Thai language?
Thai is the official language of Thailand. In a narrow sense, it refers specifically to Central Thai (Standard Thai), which is based on the Bangkok dialect and is used in official documents, media, and formal settings. In a broader sense, "Thai" can refer to all Tai languages spoken within Thailand, including Northern Thai and Isan (Northeastern Thai). The term may even extend to Tai languages outside of Thailand, such as Lao (Laotian) and Shan (spoken in Myanmar).
Thai and Lao are mutually intelligible and considered dialectal variants of the same linguistic family. Many Lao speakers can understand and speak Thai fluently, even without formal education in the language. However, due to political distinctions, Thai and Lao are officially recognized as separate national languages.
Thai has been heavily influenced by Sanskrit and Pali, incorporating a significant number of loanwords from these ancient languages. Additionally, Thai has borrowed extensively from English, Khmer, Burmese, Chinese, Malay, and even Japanese. In fact, foreign loanwords make up nearly two-thirds of the Thai vocabulary.
Thai Script
Thai uses the Thai script, which is believed to have been derived from the Khmer script, an Indic-based writing system.
The Thai script consists of 42 consonant letters, combined with vowel symbols and tone marks, forming a phonetic writing system.
How to Say “Hello” in Thai
สวัสดี/sà.wàt.dīː/
Primary Regions of Use
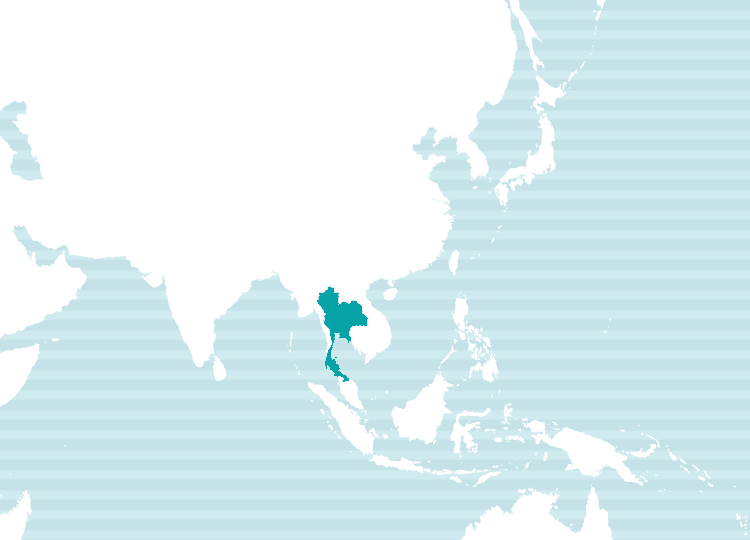
Language Family: Tai-Kadai → Kam-Tai
Spoken In: Thailand (Central Thai, Northern Thai, Southern Thai, Isan), Laos (Lao), Myanmar’s Shan State (Shan), Southern China, parts of Vietnam, and more.
Key Features of the Vietnamese Language
Why Is Thai Considered Difficult?
Thai is often regarded as a difficult language, primarily due to its complex tonal system and intricate script.
1. Tonal Challenges
Thai is a tonal language, meaning that pitch variations change the meaning of words. It has five tones, and mispronouncing them can result in completely different meanings. This makes listening to and speaking Thai particularly challenging for learners.
2. The Thai Script
The Thai writing system consists of three key elements: consonants, vowels, and tone markers. Even native Thai speakers require considerable time to fully master it. Unlike English, Thai does not use spaces between words, nor does it distinguish between uppercase and lowercase letters.
3. Simple Grammar
Despite its complex pronunciation and writing system, Thai grammar is relatively simple. Unlike English, Thai has no pronoun variations like "I, my, me, mine", and verbs do not conjugate for past or future tense. This means that even a basic word order can still convey meaning effectively.
4. Gendered Speech & Politeness
Similar to Japanese, where men often use "僕" (boku) and women use "私" (watashi), Thai also has gendered pronouns:
- Men say: ผม (phom)
- Women say: ดิฉัน (dichan)
Thai also has polite sentence endings, which differ by gender:
- Women use: ค่ะ (ka)
- Men use: ครับ (krab or khrap)
For example, when greeting someone:
Men say: "Sawadee krab" (สวัสดีครับ)
Women say: "Sawadee ka" (สวัสดีค่ะ)


